Antibiotics are medicines used to treat infections or diseases caused by bacteria (e.g. respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia and whooping cough). Antibiotics are used for a range of other infections caused by bacteria, including urinary tract infections, skin infections and infected wounds.
How do antibiotics work?
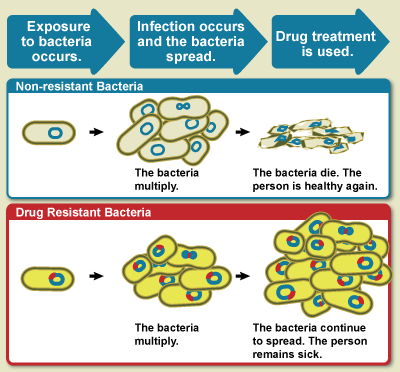
Some antibiotics work by killing germs (bacteria or the parasite). This is often done by interfering with the structure of the cell wall of the bacterium or parasite. Some work by stopping bacteria or the parasite from multiplying.
Ok What if a Antibiotics does not works on your body?Is it really possible that antibiotics does not works on our body.
Well, the answer is YES !!
Here is a case that happened in United States.
And such infections it maybe Bacteria or Virus ,and its termed as "Super Bug"
A woman in the US died after being infected by a superbug during her visit to India, say doctors who found that the ‘nightmare’ bacteria was resistant to all available antibiotics.
The infection was caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), a multidrug-resistant organism associated with high mortality.
While CRE are not new to the US, what was new in this case is that the infection was resistant or non-susceptible to all available antimicrobial drugs, researchers said.
The 70-year-old patient in the US was admitted to an acute care hospital last year after an extended trip to India.
She was given a primary diagnosis of systemic inflammatory response syndrome, likely resulting from an infected right hip seroma. The infection was serious – none of the 14 antibiotics physicians used to treat the woman worked.
After the CRE – identified as Klebsiella pneumoniae – was confirmed by lab testing, an isolate from a wound specimen was sent to the US Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for further susceptibility testing and to determine the mechanism of resistance.
That testing confirmed the presence of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM-1), an enzyme that directly breaks down carbapenems, a powerful class of antibiotics that are often used to treat multidrug-resistant infections.
The CDC’s antimicrobial testing showed the isolate was resistant to 26 different antibiotics, including all aminoglycosides and polymixins – another class of last-resort antibiotics.
It was also intermittently resistant to tigecycline, an antibiotic developed specifically to overcome drug-resistant organisms. Essentially, there were no treatment options.
Meanwhile, the patients condition was deteriorating quickly. She died of septic shock in early September last year, less than two months after admission.
The woman had been in India for two years and had been hospitalized at least four times for a right femur fracture and a subsequent hip fracture.
“We feel comfortable saying that she most likely obtained the bug in India,” said Lei Chen, senior epidemiologist with the Washoe County Health District in the US.
CRE have been labelled as a “nightmare” bacteria not only because they are already resistant to most antibiotics, but also because they spread easily in hospital settings.

No comments:
Post a Comment