An 18-year-old Indian-American girl has invented a super-capacitor device that could potentially charge your cellphone in less than 20 seconds.
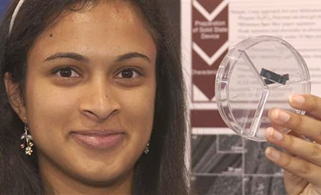
Eesha Khare, from Saratoga, California, was awarded the Young Scientist Award by the Intel Foundation after developing the tiny device that fits inside mobile phone batteries, that could allow them to charge within 20-30 seconds.
The so-called super-capacitor, a gizmo that can pack a lot of energy into a tiny space, charges quickly and holds its charge for a long time, NBC News reported.
Khare has been awarded USD 50,000 for developing the tiny device. She has also attracted the attention of tech giant Google for her potentially revolutionary invention.
According to Khare, her device can last for 10,000 charge-recharge cycles, compared with 1,000 cycles for conventional rechargeable batteries.
"My cellphone battery always dies," she said when asked about what inspired her to work on the energy-storage technology.
Super-capacitors allowed her to focus on her interest in nanochemistry "really working at the nanoscale to make significant advances in many different fields."
The gadget has so far only been tested on an LED light, but the good news is that it has a good chance of working successfully in other devices, like mobile phones, the report said.
Khare sees it fitting inside cellphones and the other portable electronic devices proliferating in today's world.

"It is also flexible, so it can be used in rollup displays and clothing and fabric. It has a lot of different applications and advantages over batteries in that sense," Khare added
Technical specifications:
In her project summary, Khare has clearly mentioned her objectives, methods and results.
Her goal was to design and synthesise a super capacitor with increased energy density while maintaining power density and long cycle life.
She designed, synthesised and characterised a novel core-shell nanorod electrode with hydrogemated TiO2(H-TiO2) core and polyaniline shell. H-TiO2 acts as the double layer electrostatic core.
Good conductivity of H-TiO2 combined with the high pseudo capacitance of polyaniline results in significantly higher overall capacitance and energy density while retaining good power density and cycle life.
This new electrode was fabricated into a flexible solid-state device to light an LED to test it in a practical application.
Khare then evaluated the structural and electrochemical properties of the new electrode. It demonstrated high capacitance of 203.3 mF/cm2 (238.5 F/g) compared to the next best alternative super capacitor in previous research of 80 F/g, due to the design of the core-shell structure.
This resulted in excellent energy density of 20.1 Wh/kg, comparable to batteries, while maintaining a high power density of 20540 W/kg. It also demonstrated a much higher cycle life compared to batteries, with a low 32.5% capacitance loss over 10,000 cycles at a high scan rate of 200 mV/s.
Therefore, she successfully managed to introduce this new energy device to replace conventional batteries in flexible electronic devices.
Charge your cellphone in less than 20 seconds